In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing and web development, understanding the tools at your disposal can make all the difference in how effectively your website performs. When it comes to guiding search engines and users through the labyrinth of your online content, sitemaps are your best friends. But here’s the million-dollar question: should you opt for an HTML sitemap or an XML sitemap? Each has its own unique strengths and shines in different scenarios, but choosing the right one can significantly impact your website’s visibility and user experience. In this article, we’re going to break down the key differences between HTML and XML sitemaps, helping you decide which option will best enhance your website’s structure and boost your SEO efforts. So,let’s dive in and uncover which sitemap is the right fit for your online presence!
Understanding the Basics of HTML and XML Sitemaps
When delving into the realm of website optimization, understanding the distinction between HTML and XML sitemaps is crucial for any web developer or digital marketer. While both serve to enhance a site’s visibility and SEO performance, they cater to different audiences and functionalities.
HTML sitemaps are primarily designed for users. They provide a structured layout of your website’s content, allowing visitors to navigate easily. By presenting links to key pages in a clear format, HTML sitemaps enhance user experience and can lower bounce rates. Here are some essential features:
- User-pleasant: Simplifies navigation for visitors.
- SEO benefits: Helps search engines understand site structure.
- visibility: Can improve internal linking.
Conversely, XML sitemaps are tailored for search engine crawlers. They provide a detailed roadmap of your website’s pages, telling search engines about the institution of your content. This format is more technical and includes essential metadata that aids in indexing. Here are the notable characteristics:
- Search engine optimization: Directly informs search engines about page importance.
- Compliance: Helps ensure all relevant pages are indexed.
- Dynamic updates: Automatically reflects changes in site structure.
To better illustrate how these two types of sitemaps compare, here’s a simple table:
| Feature | HTML Sitemap | XML Sitemap |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Website visitors | search engines |
| Format | User-friendly links | structured data |
| Usage | Navigation aid | indexing tool |
Choosing between these two sitemaps depends on your specific needs. If your goal is to enhance user experience and provide an intuitive navigation option, an HTML sitemap is the way to go. Conversely, if you want to ensure search engines can crawl your site efficiently and index all important pages, an XML sitemap is indispensable. In many cases, utilizing both can provide a comprehensive approach to improving your site’s visibility and accessibility.
Why You Need a Sitemap for your Website
Having a sitemap is essential for any website,regardless of its size or purpose. A sitemap acts as a roadmap for search engines, guiding them through the structure of your website and ensuring that all your pages are indexed correctly. This is notably critically important for larger websites with numerous pages, where search engines might miss some content without proper guidance.
There are two primary types of sitemaps: HTML and XML, each serving a distinct purpose. an HTML sitemap is designed for human visitors, providing an organized layout of your website’s pages. It improves user experience by allowing visitors to easily navigate through your content. On the other hand, an XML sitemap is intended for search engines. It contains essential metadata about your site’s pages, which helps search engines understand your content hierarchy and prioritize crawling.
Utilizing a sitemap can significantly enhance your site’s SEO performance. Consider the following benefits:
- Improved Indexing: A well-structured sitemap ensures that search engines can discover all your web pages, increasing the likelihood of being indexed.
- Faster Crawling: With a sitemap, search engines can navigate through your site more efficiently, which can lead to quicker updates and rankings.
- Content Visibility: It highlights your most important pages, helping search engines prioritize them in search results.
Moreover, having both an HTML and XML sitemap can provide the best of both worlds. While the HTML version enhances user navigation, the XML version focuses on search engine optimization. This dual approach not only boosts your visibility in search results but also enhances the user experience on your site.
| Type of Sitemap | Purpose | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| HTML Sitemap | Improves user navigation | Visitors |
| XML Sitemap | Guides search engines | SEO |
a sitemap is not just an optional feature; it is indeed a crucial component of a prosperous website strategy. By leveraging both HTML and XML sitemaps, you can enhance your site’s accessibility and ensure that your content is readily available to both users and search engines alike.

The Key Differences Between HTML and XML Sitemaps
When diving into the realm of sitemaps, it’s essential to understand the nuances between HTML and XML formats. Each serves a unique purpose, catering to different audiences and objectives. While both types aim to improve website navigation and SEO,their applications and benefits vary significantly.
HTML sitemaps are designed primarily for users, acting as an interactive guide to your website’s structure. they help visitors quickly locate content and navigate through your pages. Key features include:
- User-Friendly: These sitemaps are visually engaging and easy to read, providing a clear pathway for users.
- SEO Benefits: While not as impactful as XML sitemaps, they still contribute positively to your website’s SEO by enhancing user experience.
- Page Finding: They allow visitors to discover pages that might not be linked elsewhere on the site, increasing overall engagement.
On the other hand, XML sitemaps are tailored for search engines, focusing on the technical side of your website. They provide valuable information that helps search engines crawl and index your site more efficiently. Consider the following attributes:
- Search Engine Optimization: XML sitemaps are crucial for SEO,as they inform search engines about your website’s structure and the frequency of updates.
- Data Richness: They can include metadata such as the last modified date and the priority of pages, which aids search engines in making better indexing decisions.
- Automation: Typically generated automatically, XML sitemaps can be easily updated to reflect changes on your website, ensuring search engines have the most current information.
To illustrate the differences between these two sitemap types,here’s a brief comparison:
| Feature | HTML Sitemap | XML Sitemap |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Website Visitors | Search Engines |
| Format | User-Friendly HTML | Structured XML |
| Purpose | Navigation Aid | Indexing Aid |
| SEO Impact | Moderate | High |
while both HTML and XML sitemaps are effective tools in their own right,their distinct functionalities make them suitable for different scenarios. depending on your goals, you may choose to implement one or both types to enhance user experience and improve your site’s visibility on search engines. Understanding these differences is key to leveraging sitemaps effectively.
When to Use an HTML Sitemap for Enhanced User Experience
In the quest to enhance user experience on your website, HTML sitemaps play a crucial role. These visual representations of your site’s structure not only help search engines crawl your pages more effectively but also provide a straightforward navigation tool for your visitors. While XML sitemaps are essential for SEO, HTML sitemaps are designed specifically with the user in mind.
Here are some scenarios where implementing an HTML sitemap can significantly benefit your audience:
- Large websites: For websites with numerous pages, an HTML sitemap simplifies navigation, allowing users to find what they need quickly.
- Content-Rich Sites: Blogs and media sites that frequently update content can utilize sitemaps to showcase the latest articles, helping users discover new material.
- Complex Structures: E-commerce platforms with various categories and products can leverage an HTML sitemap to guide users through different sections without getting lost.
- Accessibility Needs: Users with disabilities may find HTML sitemaps easier to navigate, enhancing their overall browsing experience.
When designing an HTML sitemap, consider using a clear and intuitive layout that categorizes pages logically.Here’s a simple table showcasing effective categories for an HTML sitemap:
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Homepage | Welcome, About Us |
| Products | categories, New Arrivals |
| Blog | Latest posts, Popular Topics |
| Customer Service | FAQs, Contact Us |
Incorporating an HTML sitemap not only helps your users but also reflects your commitment to providing a seamless browsing experience. By ensuring that visitors can easily access all areas of your site, you increase the likelihood of them staying longer, exploring more pages, and ultimately converting. So,when you’re looking to boost user engagement and satisfaction,don’t overlook the power of an HTML sitemap.
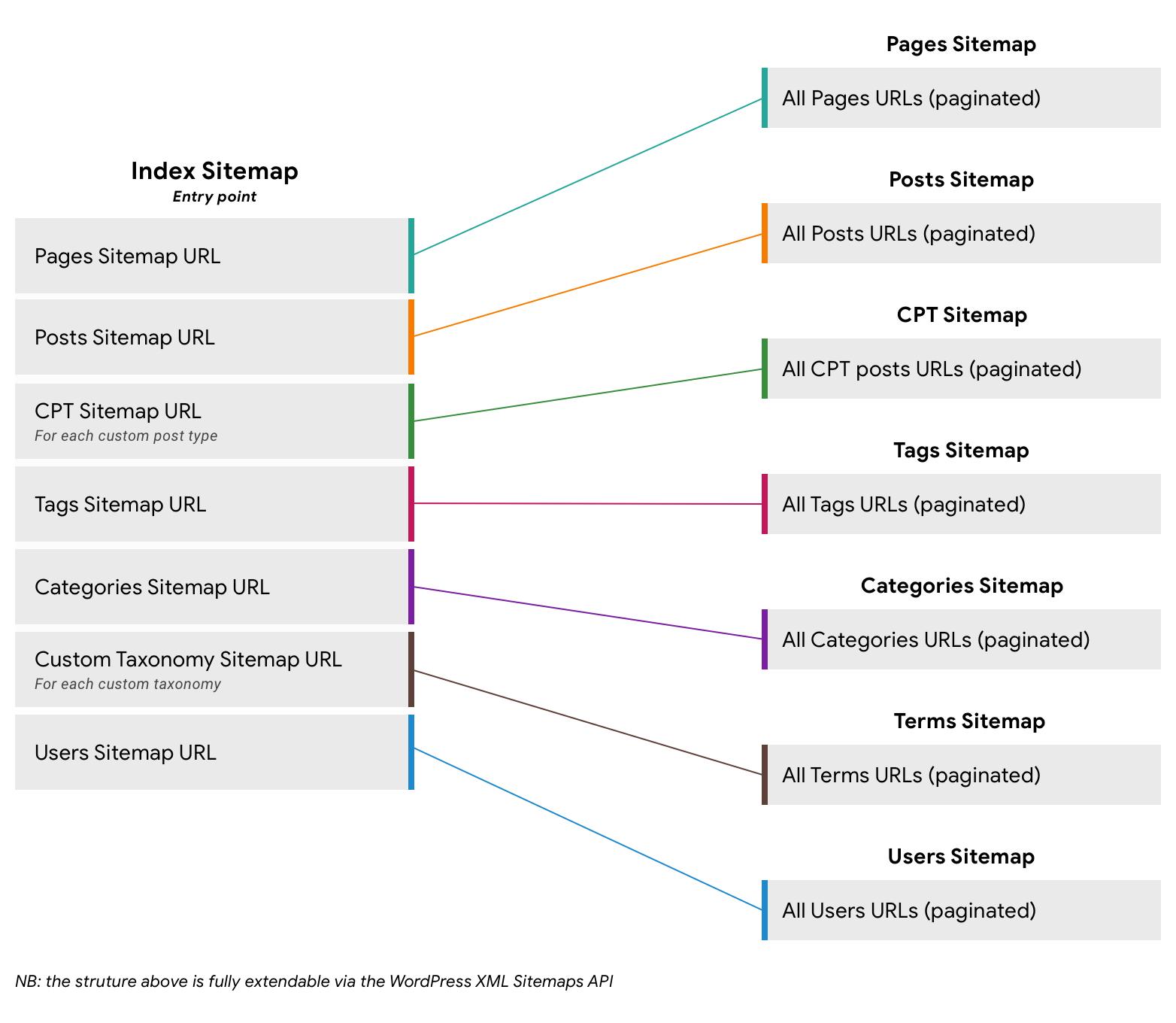
The Benefits of Choosing an XML Sitemap for SEO
When it comes to optimizing your website for search engines, choosing the right type of sitemap can make a world of difference. An XML sitemap specifically caters to the needs of search engines, offering a structured format that allows them to crawl and index your site efficiently. This structured approach can significantly enhance your site’s visibility in search results.
Here are some key benefits of opting for an XML sitemap:
- Improved Indexing: XML sitemaps provide search engines with a clear path to discover all your pages, including those that may be buried deep within the site structure.
- Prioritization of Content: You can specify the importance of different pages, allowing search engines to focus on what matters most to your business.
- Update Notifications: With an XML sitemap, you can inform search engines about recent changes or new content, ensuring that your freshest updates are indexed promptly.
- Support for Multimedia Content: XML sitemaps can include information about images, videos, and other media, enhancing your content’s discoverability.
Another advantage of using an XML sitemap is its compatibility with various protocols and search engines. Unlike HTML sitemaps, which are primarily designed for visitors, XML sitemaps serve a technical purpose that caters specifically to crawlers.This means that even if your site has complex navigation or dynamic content, an XML sitemap can simplify the crawling process.
For those managing large websites, the benefits multiply. Large-scale sites often present unique challenges regarding indexing, and an XML sitemap can efficiently handle pagination and ensure that all essential pages are accounted for. This is especially crucial for e-commerce sites with numerous product pages.
| Feature | XML Sitemap | HTML Sitemap |
|---|---|---|
| Designed for Search Engines | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Facilitates Page Prioritization | ✔️ | ❌ |
| Supports Media Content | ✔️ | ❌ |
| User-Friendly Navigation | ❌ | ✔️ |
an XML sitemap not only enhances your SEO strategy but also provides clear advantages in visibility and indexing. if you’re serious about improving your site’s search engine performance, incorporating an XML sitemap into your strategy is a wise decision.
How Search Engines Interpret HTML and XML Sitemaps
When it comes to how search engines interpret sitemaps, the distinction between HTML and XML formats is crucial. Search engines like Google utilize these sitemaps to understand the structure and hierarchy of a website, which directly impacts indexing and ranking. An HTML sitemap is primarily designed for human users, providing a user-friendly way to navigate through site content. it’s visually appealing and can improve user experience by making information easily accessible. However, it doesn’t carry the same weight with search engines as an XML sitemap does.
On the other hand,an XML sitemap is tailored specifically for search engines.This format provides a more comprehensive and structured overview of your website’s pages, allowing search engines to crawl them more efficiently. It includes vital metadata about each URL, such as:
- Last modified date – Indicates when a page was last updated.
- Priority - Suggests the importance of a page relative to others on the site.
- Change frequency – tells search engines how often the content is expected to change.
Search engines parse XML sitemaps to prioritize crawling, ensuring that the most critically important pages are indexed first. This is particularly beneficial for large websites with numerous pages,where some content might potentially be more crucial to user queries then others. In contrast, an HTML sitemap might potentially be ignored by search engines or not fully utilized, which could lead to missed opportunities for indexing all your valuable pages.
To illustrate the differences, consider the following table:
| Feature | HTML Sitemap | XML Sitemap |
|---|---|---|
| User Focus | Human visitors | Search engines |
| Format | Visual, easy to navigate | Structured, data-centric |
| Indexing Impact | Minimal | Meaningful |
| Metadata Support | None | Extensive |
Ultimately, incorporating both types of sitemaps can enhance your website’s visibility and usability. By providing an HTML sitemap, you cater to your visitors’ navigation needs. Meanwhile, the XML sitemap ensures that search engines have a clear path to your most important content, optimizing your chances of ranking higher in search results.
Best Practices for Creating an Effective Sitemap
Creating an effective sitemap is crucial for enhancing your website’s visibility and facilitating better indexing by search engines. To achieve this,consider implementing the following best practices:
- Prioritize pages: Include only the most important pages of your site in the sitemap. This helps search engines focus on the content that matters most to your audience.
- Keep it simple: Ensure that the sitemap is easy to navigate. A well-organized structure allows both users and search engines to find information quickly.
- Use descriptive URLs: Make sure that the URLs listed in your sitemap are clean and descriptive. This not only aids in SEO but also improves user experience.
Regularly updating your sitemap is another essential practice. Whenever you add or remove content, modify your sitemap accordingly. This keeps search engines informed about the latest changes on your site, ensuring that they index your pages accurately. Consider using automated tools that can help keep your sitemap current without much manual effort.
When it comes to choosing between HTML and XML sitemaps, understanding their purposes is key. an XML sitemap is specifically designed for search engines, providing them with a structured format of your site’s URLs, while an HTML sitemap is user-friendly, serving as a navigation aid for visitors. Each serves a unique purpose, so it’s frequently enough beneficial to use both.
| Type | Purpose | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| XML Sitemap | Search engine indexing | Website crawlers |
| HTML Sitemap | User navigation | Website visitors |
Lastly, remember to submit your sitemap to search engines like Google and Bing through their respective webmaster tools. this ensures that your content is accurately indexed and can lead to improved visibility in search results. By following these best practices, you’ll not only enhance your site’s SEO performance but also provide a better experience for your users.
Combining HTML and XML Sitemaps for Optimal Results
when it comes to optimizing your website’s visibility, leveraging both HTML and XML sitemaps can yield powerful results. Each type serves a distinct purpose, yet they complement each other in driving traffic and enhancing SEO. By combining these two formats, you can ensure that your site is easily accessible to both users and search engines alike.
HTML sitemaps are user-friendly, acting as a navigation tool that helps visitors explore your website. Here are some key benefits of using an HTML sitemap:
- Improved User Experience: Visitors can quickly find the information they need, reducing bounce rates.
- Enhanced Internal Linking: It provides additional pathways for users, which can lead to increased page views.
- boosted Engagement: By making it easier to navigate, visitors are likely to spend more time on your site.
On the other hand, XML sitemaps are essential for search engines, providing critical information about your site’s structure and content. Here’s why you should integrate an XML sitemap:
- Search Engine Indexing: It ensures that all pages are indexed efficiently, which is vital for SEO.
- priority and Frequency: You can specify the importance of pages and how often they are updated, guiding search engines effectively.
- Support for Rich Media: XML sitemaps can include details for images, videos, and other media types, enhancing discoverability.
To combine the strengths of both formats, consider creating a strategy that utilizes them in tandem. As an example, while your XML sitemap is submitted to search engines via Google Search Console, your HTML sitemap can be prominently linked within your website’s footer. This dual approach not only caters to different audiences but also maximizes your overall SEO strategy.
| Feature | HTML Sitemap | XML Sitemap |
|---|---|---|
| user Accessibility | Yes | No |
| Search Engine Optimization | Limited | High |
| Internal Linking | Yes | No |
| Rich Media Support | No | Yes |
The synergy of HTML and XML sitemaps not only enhances your site’s structure but also boosts your chances of ranking higher in search results.By providing value to both users and search engines, you’re setting your website up for optimal success. Don’t overlook the potential of these two powerful tools in your digital marketing arsenal!

Making the Right Choice: HTML vs XML sitemaps for Your Site
When it comes to enhancing your website’s visibility and user experience, choosing between HTML and XML sitemaps is crucial. Each type of sitemap serves a different purpose and understanding these can significantly impact your SEO and user engagement.
HTML Sitemaps are designed primarily for users. They provide a straightforward, navigable structure of your website’s content, making it easier for visitors to find what they’re looking for. Here are some key points:
- Improves user experience by offering easy navigation.
- Can reduce bounce rates, as users can find related content quickly.
- Encourages users to explore more pages, increasing overall page views.
Conversely,XML Sitemaps cater to search engines rather than users. They help search engine crawlers understand the structure of your site and index it more effectively. Consider the following benefits:
- Facilitates better indexing of your web pages by search engines.
- Can include additional metadata like last modified dates and priority.
- Essential for large websites with many pages, ensuring all content gets crawled.
Choosing the right sitemap may also depend on the size and complexity of your website.Below is a swift comparison to guide your decision:
| Feature | HTML Sitemap | XML Sitemap |
|---|---|---|
| User-Focused | Yes | No |
| Search Engine Friendly | No | Yes |
| Ease of Navigation | High | Low |
| Best for Large Sites | No | Yes |
using both types of sitemaps can provide a comprehensive approach to enhancing your site’s visibility and usability. Consider implementing an HTML sitemap for your visitors and an XML sitemap for search engines to reap the full benefits of improved SEO and user engagement.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Sitemap for Your Goals
When deciding between an HTML and XML sitemap, it’s essential to align your choice with your specific goals. Each type of sitemap serves distinct purposes, and understanding these can significantly enhance your website’s visibility and user experience.
HTML sitemaps are primarily designed for human visitors. They provide a clear and structured overview of your site’s content, aiding navigation and improving usability. Here are some benefits of using an HTML sitemap:
- Enhanced User Experience: Makes it easier for users to find information.
- Reduced Bounce rate: Engages visitors by offering multiple pathways to explore content.
- SEO Boost: Can improve internal linking, which is beneficial for search engines.
On the other hand, XML sitemaps are tailored for search engines. They communicate essential information about your site’s structure, helping search engine bots understand which pages are available for crawling and indexing. Consider the following advantages:
- Efficient Crawling: Ensures that all important pages are indexed quickly.
- Priority and Frequency Settings: Allows you to indicate the importance and update frequency of pages.
- Support for Multimedia Content: Helps search engines discover non-standard content types like images and videos.
Choosing the right type may also depend on the size of your website. for larger sites, combining both sitemap types can be beneficial. This approach leverages the strengths of both formats:
| Type of Sitemap | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| HTML | Users | Facilitates navigation |
| XML | Search Engines | Indexes and crawls pages |
| Combined | Both Users & Search Engines | Maximizes visibility |
Ultimately, your decision should reflect your primary objectives: If enhancing user navigation is your focus, prioritize the HTML sitemap.though, if your goal is to improve search engine visibility, an XML sitemap will be more beneficial.Assess your website’s unique needs and strike a balance that aligns with your digital strategy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q&A: HTML vs XML Sitemap: Which Should You Use?
Q: What’s the main difference between an HTML sitemap and an XML sitemap?
A: Great question! An HTML sitemap is designed primarily for human visitors. It’s a user-friendly page that lists all the pages on your website, helping users navigate easily.Conversely, an XML sitemap is meant for search engines. It’s a structured file that helps search engines like Google crawl and index your website more efficiently.Think of it as a roadmap for bots, while the HTML sitemap is more like a guide for your visitors.
Q: Why should I bother creating an HTML sitemap if I already have an XML sitemap?
A: While an XML sitemap is essential for search engines, an HTML sitemap serves a different purpose. Having an HTML sitemap enhances user experience by providing a clear layout of your site’s structure. It can reduce bounce rates by helping users find what they need more quickly. plus, it’s a great way to highlight important pages that might not be easily accessible through navigation menus. So,why not make it easier for your visitors?
Q: Are there any SEO benefits to having an HTML sitemap?
A: Absolutely! While the direct SEO impact might not be as significant as an XML sitemap,an HTML sitemap can still contribute positively. By improving user experience, you can increase the time users spend on your site, reduce bounce rates, and even encourage more backlinks if users find your content valuable. A well-structured HTML sitemap can lead to better visibility and engagement, which are valuable for SEO.
Q: How do I create an XML sitemap? Is it complex?
A: Not at all! Creating an XML sitemap can be quite simple. There are various online tools and plugins available, especially if you’re using platforms like wordpress. Most of these tools automatically generate and update your XML sitemap whenever you add new content. Just make sure you submit it to search engines via their webmaster tools, and you’re good to go!
Q: Can I use both HTML and XML sitemaps on my website?
A: Definitely! In fact, using both is a smart strategy. An XML sitemap helps search engines understand your site structure, while an HTML sitemap guides visitors. They complement each other perfectly, ensuring that both users and search engines can navigate your site easily. So why not double your chances of success?
Q: What should I keep in mind when creating an HTML sitemap?
A: When creating your HTML sitemap, focus on clarity and simplicity. Organize it logically, group similar pages together, and keep the design clean. Use descriptive titles for each link,so users know exactly what they’re clicking on. The goal is to make navigation a breeze for your visitors. Remember, the easier you make it for them, the more likely they are to stick around!
Q: If I had to choose one, which should I prioritize: HTML or XML sitemap?
A: If you can only choose one, go for the XML sitemap, especially if your primary goal is to improve search engine visibility. however, if you have the resources, I strongly recommend implementing both. They serve different purposes and can work together to enhance both your SEO efforts and user experience.In the long run, having both will pay off!
Final Thoughts:
choosing between HTML and XML sitemaps isn’t really about picking one over the other; it’s about understanding the unique benefits each offers. By leveraging both, you’re not only improving your site’s SEO but also creating a smoother experience for your visitors. So go ahead, make the most of these tools and watch your website thrive!
Key Takeaways
both HTML and XML sitemaps serve essential roles in the world of web development, but the choice between them ultimately depends on your specific goals. if you’re looking to enhance user experience and guide visitors through your website, an HTML sitemap is the way to go. It’s user-friendly and provides a clear roadmap for your content.on the other hand, if your priority is to ensure that search engines efficiently crawl and index your site, then an XML sitemap is indispensable. It’s designed specifically for search engines,giving them the information they need to understand your site’s structure and content in a more streamlined way.
Ultimately, why settle for just one when you can have both? A combination of HTML and XML sitemaps can cater to both your users and search engines, maximizing your website’s reach and usability. So,assess your needs,weigh your options,and take the next step in optimizing your online presence. Your website deserves the best tools to succeed, and the right sitemap is a critical part of that equation. Happy optimizing!